Signal filtering
[202] Capacitors are divided into polarized and non-polarized depending on whether the direction of their inclusion in the circuit is important. Generally speaking, capacitors filter the waveform of the power source. It is assumed that the longer lead from the capacitor is the positive pole, which is sometimes reflected in the marking in the diagram. Electrolytic capacitors consist of a metal cover and an electrolyte lined with paper. Non-polar (non-polarized) capacitors can be made of ceramic elements or foil. There are also tantalum capacitors which both offer high capacitance and relatively low losses. The physical size of a capacitor depends not only on its capacity but also on its maximum operating voltage.
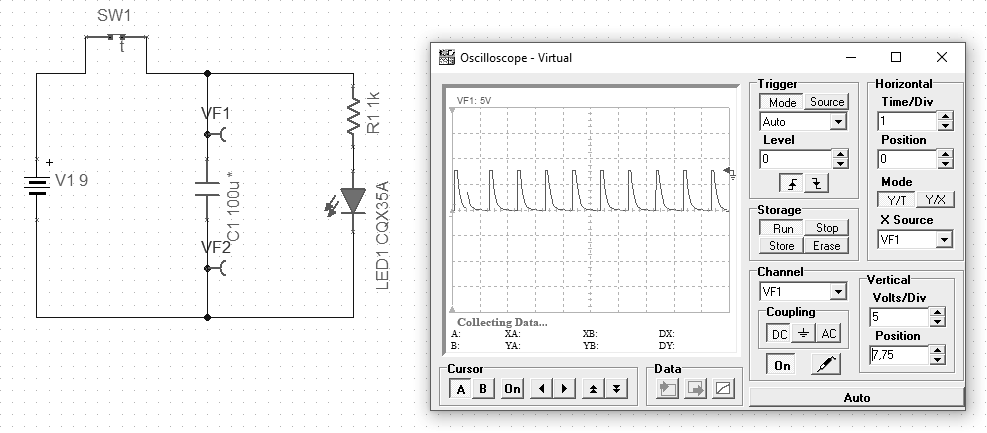
In the above example, we put a timer switch into the circuit, which in a 1 second cycle turns on for 100ms, causing the capacitor to charge. After the time specified by the parameters of the elements, the LED starts to emit light. When the switch disconnects charging, the capacitor discharges. The time of diode activation is controlled by determining the capacitance of the used capacitor.
However, the main task for capacitors is to filter the power supply. This treatment is used to protect sensitive components, e.g. a microcontroller in a digital circuit. It is most effective to use different types to filter the specific interference. Capacitors are connected to the circuit in parallel.
“A capacitor is a device for the temporary storage of electric charge. What is believed to be the first capacitor was called the Leyden jar, which was invented by Pieter van Musschenbroek in 1746 at Leyden (or Leiden) University in the Netherlands. It was a glass jar wrapped inside and out with a thin metal foil. The outer foil was bonded with the ground, and the inner foil was connected to an electricity source, such as like an electrostatic generator. Though at that time, it was not understood how it worked, experimenters found that the Leiden jar seemed to store an electric charge even when unplugged from the generator. ” [206]
Examples available at https://github.com/michalasobczak/simple_hpc/tree/master/SeriesPartOne