Distributed, partitioned, multi-master, increment horizontal scale-out NoSQL data manegement system for global mission-critical use cases handling petabyte sized datasets
Table of Contents
- Dynamo, Amazon, Facebook, Apache…
- Characteristics
- Cassandra QL quirks
- What I find interesting
- Installation in Docker/Portainer/Proxmox
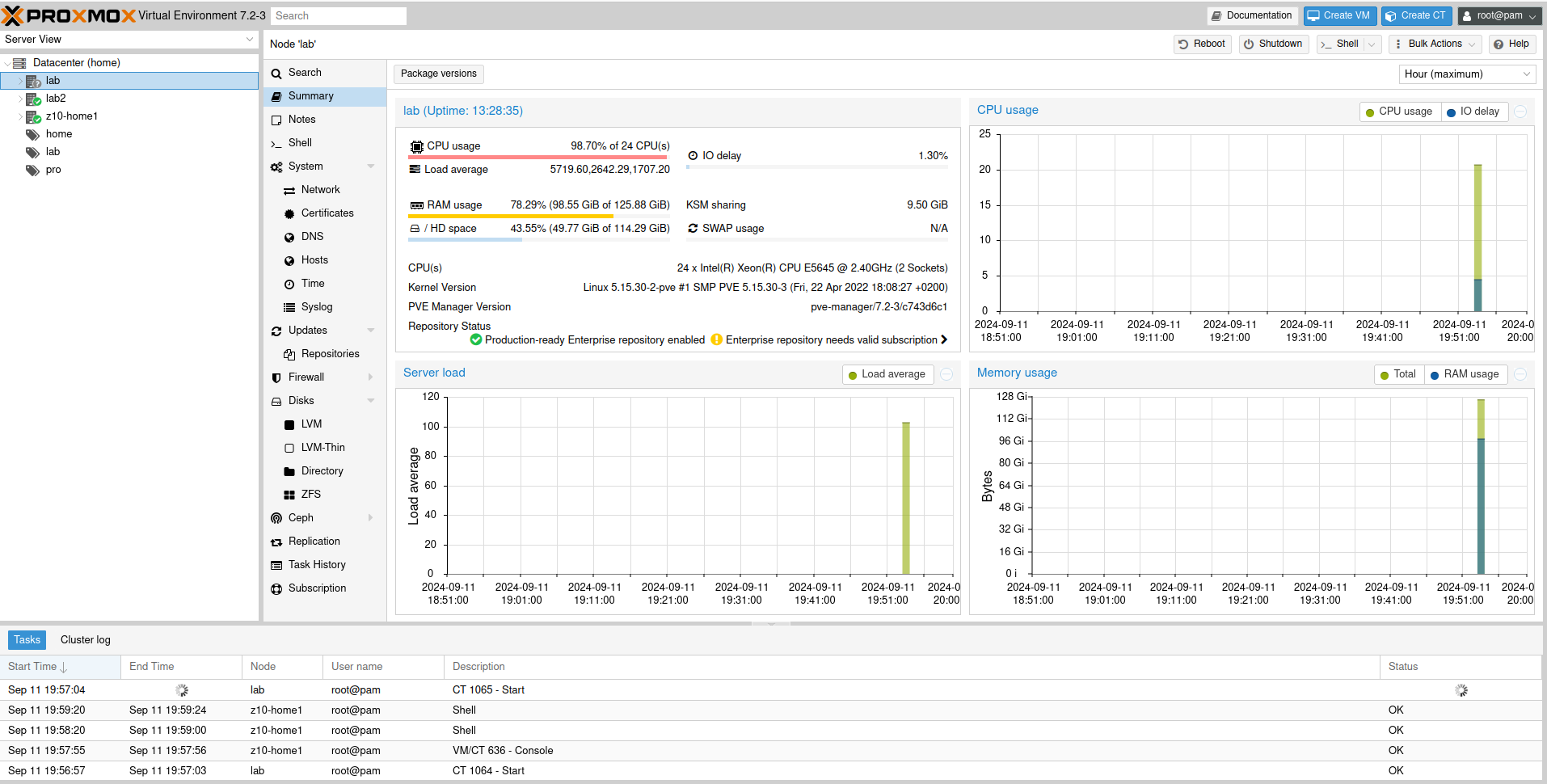
- Monitoring nodes
- Data analysis with Redash
- CQL DDL
- CQL DML
- Design principals
- Application example & flushing commitlog
Dynamo, Amazon, Facebook, Apache…
“Reliability at massive scale is one of the biggest challenges we face at Amazon“
source: “Dynamo: amazon’s highly available key-value store”
In 2004 there have been performance issues in Amazon e-commerce handling due to high traffic. By 2007 the concept of Dynamo has been materialized as Amazon S3. Then in 2008 Facebook with co-authors of Amazon Dynamo developed its own distributed NoSQL system, Cassandra. In 2009 Cassandra became Apache’s project. However, Amazon’s DynamoDB came in 2012, it also uses Dynamo concept, however it is fully proprietary solution.
So we have Dynamo concept, we have Amazon and Facebook and finally Apache Cassandra project. Without diving deep into the details of who was the first and who borrowed what… Cassandra is on the market for 16 years already (as of 2024).
Characteristics
Cassandra is meant to be run in multi-node environment and it is especially useful when running in dispersed networks. It is master-less which means that there is no single point of failure, of course only in case of proper keyspace/database and table designs especially in terms of replication factor. Having replication factor greater than 1, means that we introduce redundancy into our data layout which leads us towards resilience of a Cassandra cluster. Cassandra being distributed-capable still is visible as a single entity from user perspective.
The key concept which provides almost endless scaling capabilities is that Cassandra is distributed and uses data partitions. Comparing to RDBMS (like PostgreSQL) you need no additional configuration in order to run partitions and shards as it is built into Cassandra engine. Data in Cassandra are placed on particular nodes taking into account the partition key. If you need more storage or more computational power, you just add additional nodes to the cluster.
“Each node owns a particular set of tokens, and Cassandra distributes data based on the ranges of these tokens across the cluster.”
source: cassandra.apache.org/_/cassandra-basics.html
Data is spread across cluster based on partition key which is a hash-function value of data key which then maps to nodes which hold this particular tokens. Any node act as a coordinator looking for target node and gossiping with other nodes about cluster structure. There are of course many challanges, for instance when you defined replication factor > 1 and experience some networking issues. Transactions may or may not be successful depending on configuration, how many of nodes responded to transaction and confirmed it.
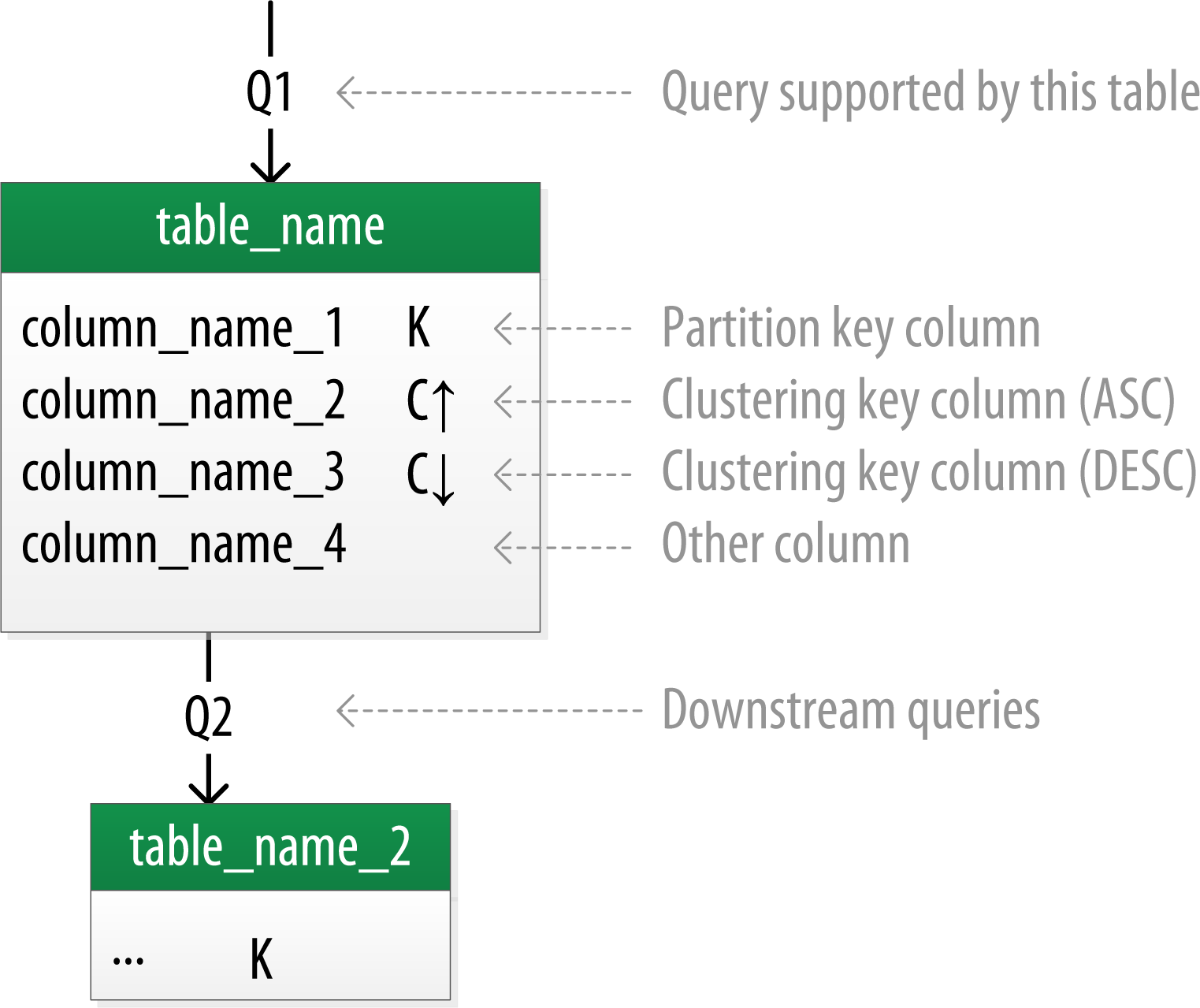
source: https://cassandra.apache.org/doc/stable/cassandra/data_modeling/data_modeling_logical.html
Concerning data placement strategy: for non-production or simple production setups you can use SimpleStrategy, however for bigger production setups it is recommended to use NetworkTopologyStrategy which take into consideration DC and Rack definitions.
“Data modeling that considers the querying patterns and assigns primary keys based on the queries will have the lowest latency in fetching data”
source: cassandra.apache.org/doc/stable/cassandra/cql/ddl.html
And how data is organized into files?
“Sorted Strings Table (SSTable) is a persistent file format used by ScyllaDB, Apache Cassandra, and other NoSQL databases to take the in-memory data stored in memtables, order it for fast access, and store it on disk in a persistent, ordered, immutable set of files. Immutable means SSTables are never modified. They are later merged into new SSTables or deleted as data is updated.”
source: www.scylladb.com/glossary/sstable/
Cassandra QL quirks
Keep mind that…
“The append and prepend operations are not idempotent by nature”
“lists have limitations and specific performance considerations that you should take into account before using them”
Currently, aliases aren’t recognized in the
WHEREorORDER BYclauses in the statement. You must use the orignal column name instead.
The primary key uniquely identifies a row in the table, as described above. A consequence of this uniqueness is that if another row is inserted using the same primary key, then an UPSERT occurs and an existing row with the same primary key is replaced. Columns that are not part of the primary key cannot define uniqueness.
…but as Cassandra allows the client to provide any timestamp on any table, it is theoretically possible to use another convention. Please be aware that if you do so, dropping a column will not correctly execute.
What I find interesting
I think that worth noticing is speculative_retry feature which defines when query coordinator could query another node for data in case of slow response or unavailability of some node.
Worth trying out is Vector Search feature:
Vector Search is a new feature added to Cassandra 5.0. It is a powerful technique for finding relevant content within large datasets and is particularly useful for AI applications.
I find in documentation that it is not recommended to run Cassandra on NFS/SAN as the whole Cassandra distrubuted concept relies on separated nodes. However it also told that Cassandra will better perform in RAID0 or JBOD (Just Bunch Of Disk) rather than on RAID1 or RAID5. Well… that is obvious that things run better without additional overhead, and I think that it should be stated that this suggestion is valid only if we aim for maximum performance sacrificing a little bit of security.
Installation in Docker/Portainer/Proxmox
In order to start with Cassandra we can use Proxmo virtual environment and Docker Swarm with Portainer on top of it. However, there are some certain issues with running it in Swarm mode. Long story short, Swarm adds additional ingress layer which adds additional IP addresses to the container. It somehow confuses Cassandra. I belive that there is some solution for this, however I found few bug reports in this matter without clear conclusion.
So, we can stay with Swarm mode, but deploy Cassandra as regular container, not a service. Yes, we can run regular containers without putting them into services while running in Swarm mode.
I will use previously prepared Docker Swarm cluster.
For this deployment I will go for Docker image cassandra:5.0.0:
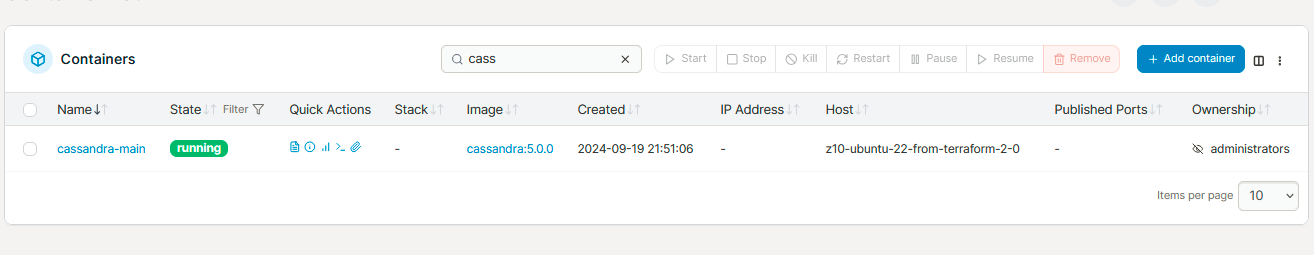
And here it starts:
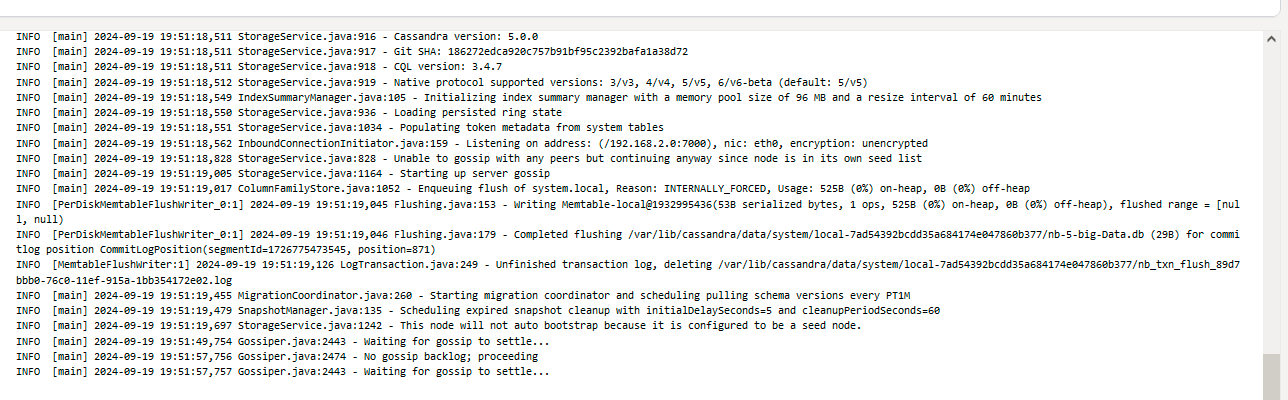
Every Cassandra node should open port 7000 for inter-node communication. Port 9042 is for query handling.
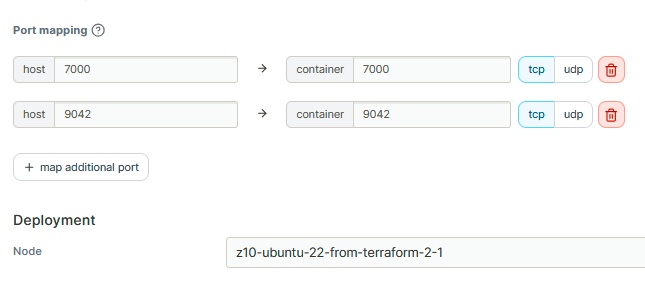
We need to point exact Docker Swarm node on which we would like to place our Cassandra node. Then in environments section define CASSANDRA_BROADCAST_ADDRESS and CASSANDRA_SEEDS. It is important to pass seed nodes cross cluster, so in case of outage everything left in the cluster should remain operational.
Monitoring nodes
Every node container contains nodetool utility which helps identifing status of our Cassandra cluster. We can query for general status (status command), detaled info (info command), initialite compatcion (compact command) and many many more.
cd /opt/cassandra/bin
./nodetool status
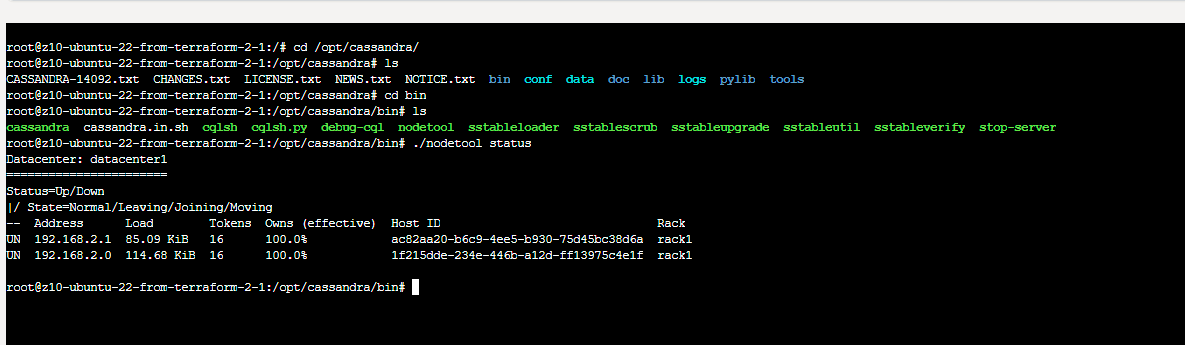
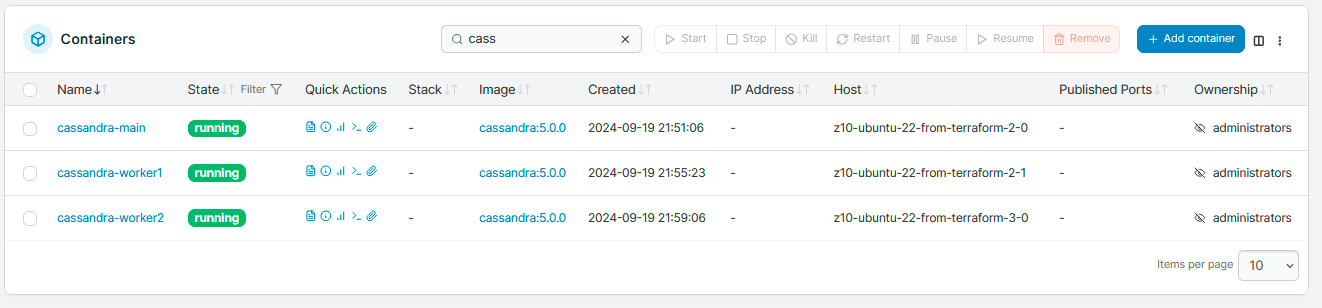
For this demo I decide to go for simple strategy cluster with one main node for seeding and two workers.
Data analysis with Redash
To query Cassandra you can use either CQLSH (present on every Cassandra node, /opt/cassandra/bin) or install Redash. It is a complete data browsers and visualizer with ability to connect to all major RDBMS and to Cassandra also. To install redash download https://github.com/getredash/setup repository and follow instructions.
To start playing with CQL (Cassandra Query Language) we need to define keyspace (using CQLSH), which is some sort of database. We define it as SimpleStrategy with 3 copies. So all of our data will be spread on all cluster nodes. This way we will be resilient of hardware or network failure. For more complex scenarios use NetworkTopologyStrategy with defined DC and Rack parametrs.
create keyspace domains
with replication = {
'class: 'SimpleStrategy',
'replication_factor': 3
};
Now, once we created keyspace, we can go to Redash and define Data Source.
Then, start new query and play around.
CQL DDL
We already created keyspace/database, and it time to create table with single-column primary key.
create table mylist
(
myid int primary key,
mytext text
)
In return in Redash you will get:
Error running query: 'NoneType' object is not iterable
which means that Redash expects to receive an iterable object and instead of got nothing, because creating table or keyspaces returns nothing.
CQL DML
Cassandra restricts user as it limits possiblities to query for data only if clause matches primary key columns.
insert into mylist (myid, mytext) values (1, 'test 1');
insert into mylist (myid, mytext) values (2, 'test 2');
select * from mylist where myid = 1;
select * from mylist where myid in (1,2);
Take another example:
create table myotherlist (
myid int,
myotherid int,
mylastid int,
primary key (myid, myotherid, mylastid)
);
Then insert some data:
insert into myotherlist (myid, myotherid, mylastid) values (1, 1, 1);
insert into myotherlist (myid, myotherid, mylastid) values (2, 2, 2);
insert into myotherlist (myid, myotherid, mylastid) values (3, 3, 3);
insert into myotherlist (myid, myotherid, mylastid) values (4, 4, 4);
And then try various combinations of where clause. The following will return error “column cannot be restricted as preceding column is not restricted”. It means that it does not have individual indices which could help locate those different column values. Instead it seems that it have some kind of tree-like index structure (Log Structured Merge Tree to be specific) which can be traversed only by using all consecutive and adjacent primary key ingredients:
select * from myotherlist where mylastid = 1;
But this one will work:
select * from myotherlist where myid = 1;
select * from myotherlist where myid = 2 and myotherid = 2;
select * from myotherlist where myid = 3 and myotherid = 3 and mylastid = 3;
As primary key must be unique then you cannot insert same values in all columns which already exist in a table. Moreover, you cannot skip any or required clustering keys (myotherid and mylastid).

Same applies with partition key (myid):

Design principals
Contrary to RDBMS, Cassandra’s design principals are focused more on denomalization than normalization. You need to design your data model by the way you will be using it, intead of just describing the schema.
By contrast, in Cassandra you don’t start with the data model; you start with the query model
The sort order available on queries is fixed, and is determined entirely by the selection of clustering columns you supply in the
CREATE TABLEcommand
In relational database design, you are often taught the importance of normalization. This is not an advantage when working with Cassandra because it performs best when the data model is denormalized.
A key goal that you will see as you begin creating data models in Cassandra is to minimize the number of partitions that must be searched in order to satisfy a given query. Because the partition is a unit of storage that does not get divided across nodes, a query that searches a single partition will typically yield the best performance.
Application example & flushing commitlog
So, previously I defined table called myotherlist with three integer colums contained in primary key. Let’s use Python to insert some data. First install the driver:
pip3 install cassandra-driver
Then define the program. We are going to use prepared statements as they save CPU cycles.
import cassandra
print(cassandra.__version__)
from cassandra.cluster import Cluster
cluster = Cluster(['192.168.2.0', '192.168.2.1', '192.168.3.0'])
session = cluster.connect()
ret = session.execute("USE domains")
rangeofx = range(100)
rangeofy = range(100)
rangeofz = range(100)
stmt = session.prepare("INSERT INTO myotherlist (myid, myotherid, mylastid) values (?, ?, ?)");
for x in rangeofx:
for y in rangeofy:
for z in rangeofz:
print(x, y, z)
session.execute(stmt, [x, y, z])
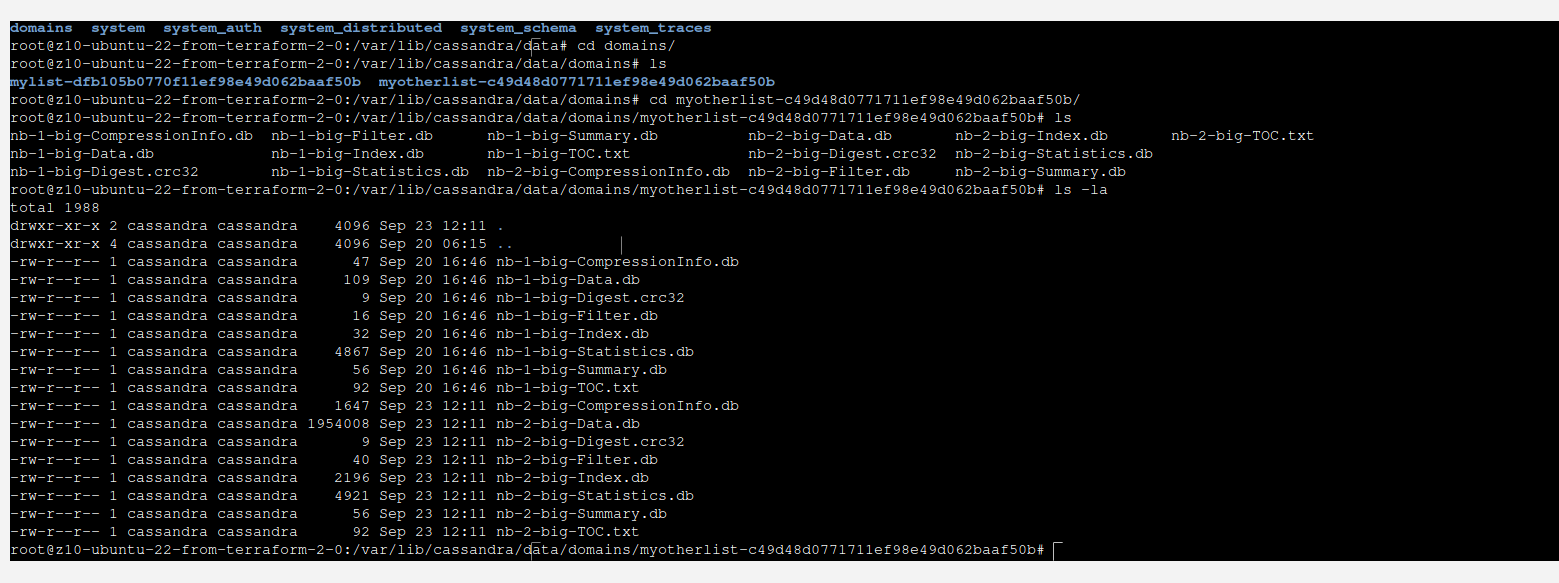
It is quite interesting that those data will not be present in data file instantly. Instead they will appear in commitlog, lets take a look:
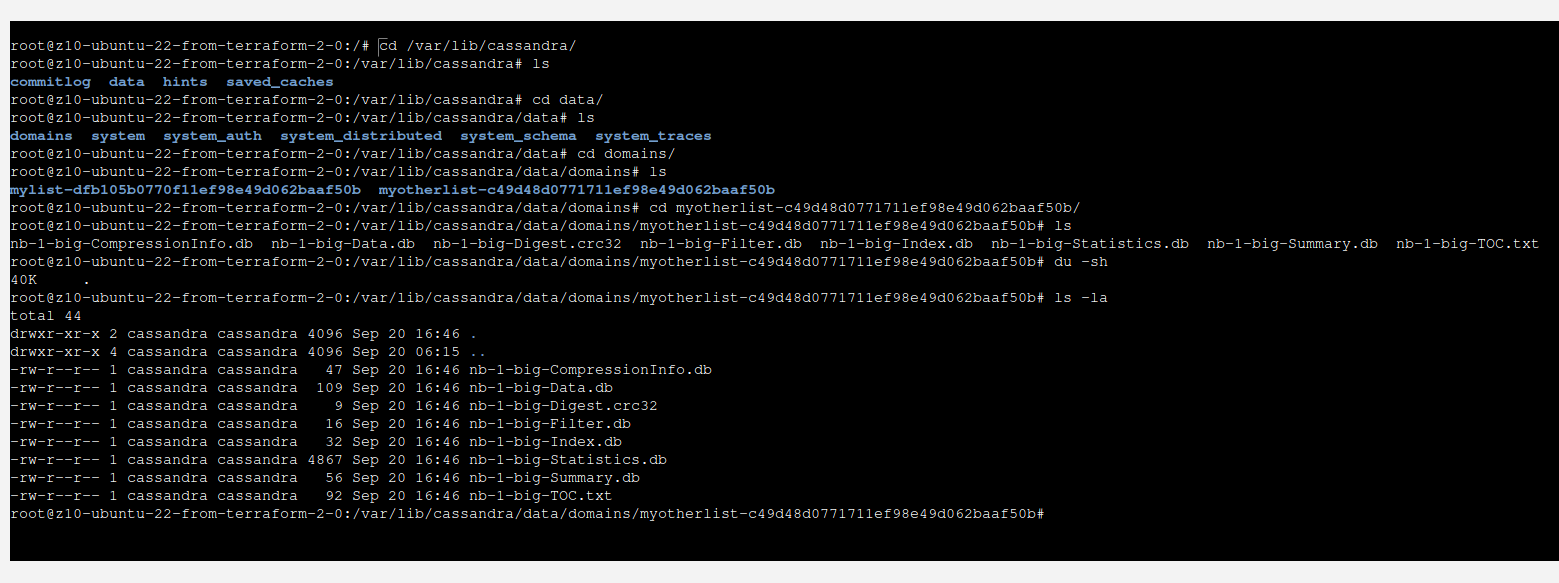
You can see that there is not much happening here. However, when we take a look at commitlog, we can see that most probably there is our data located.
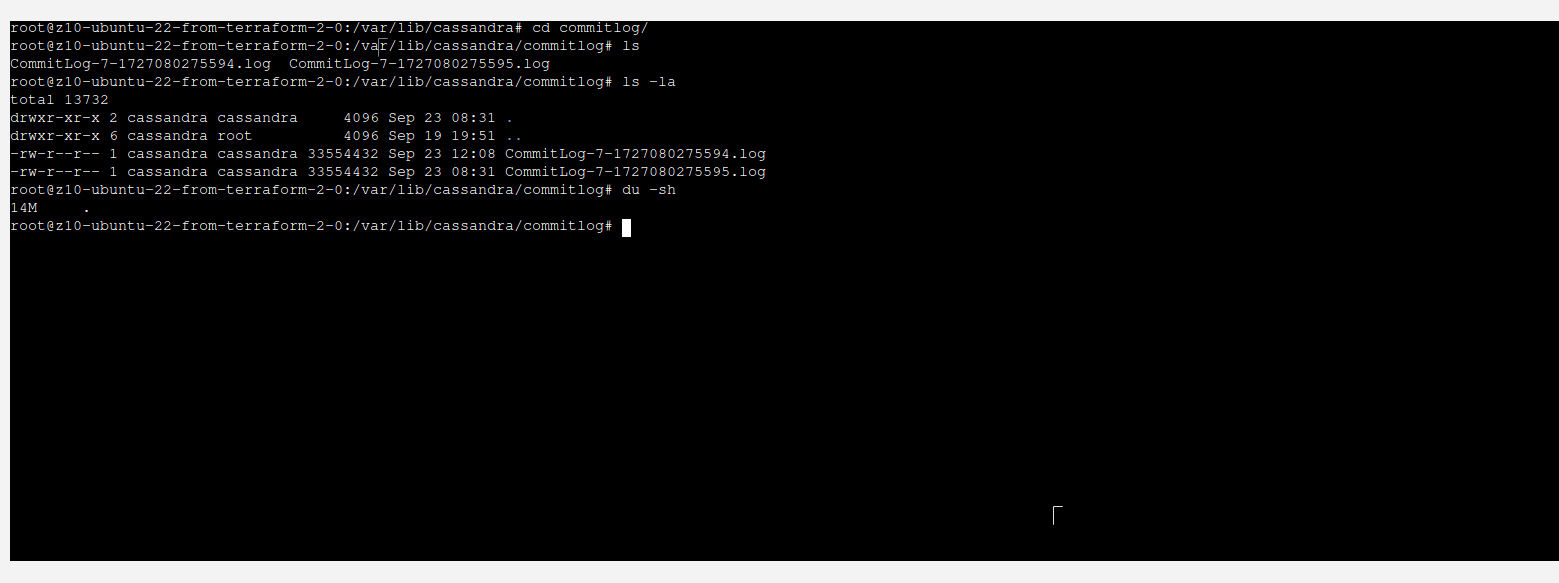
In order to write our data into SSTable files, you run ./nodetool flush. This will move memory and commitlog into data file.